Innovative services deployed by the Museum to its visitors are based on location and context-aware paradigm. Such as Navigation and Assisted Guide systems, Recommendation and Advertising engines
We study solutions for real needs, defined by domain experts and modeled by our research group. Proposed methods and technologies are always validated in the real environment
Museums host many direct and indirect services, our researcher apply new techniques and technologies to offer innovative, low-cost and efficient solutions in the field of occupancy estimation, people counting, security systems, energy management
We always try to exploit existing infrastructures and data for providing innovative, low-cost services. For example, in our publications we proved how standard environmental monitoring can be applied in different fields such as Occupancy Estimation
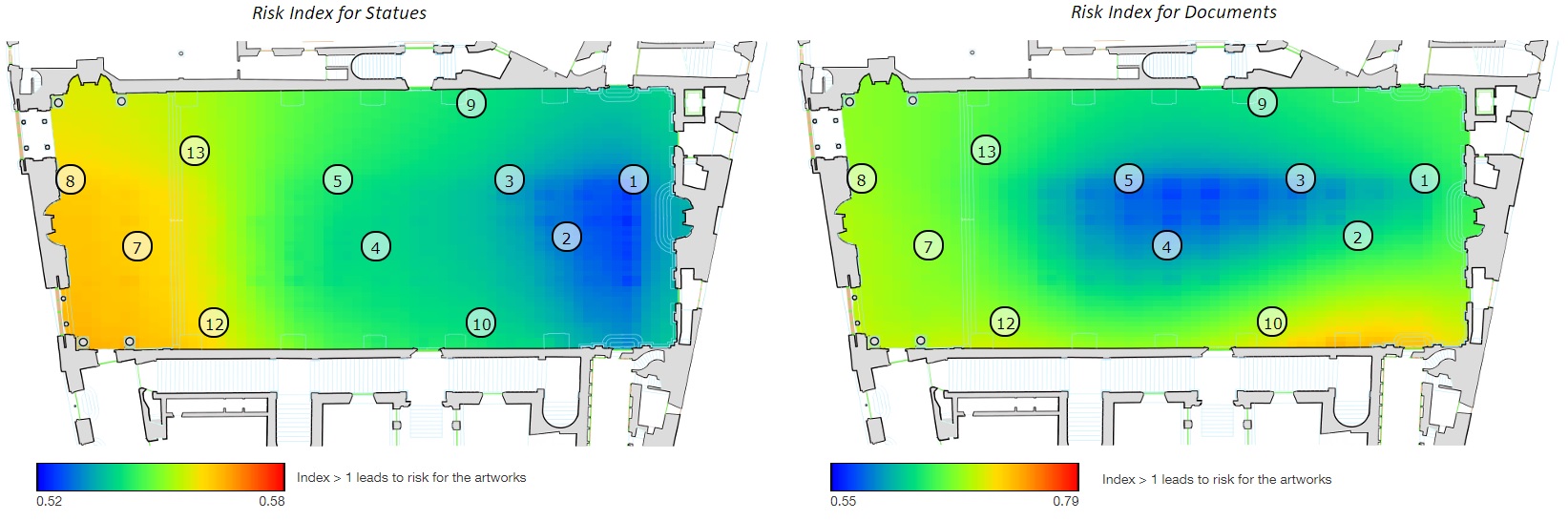
Monitor temperature and humidity in order to check the conditions and the safety of artworks
IoT & WSN technology coupled with MEMs accelerometer and environmental sensors
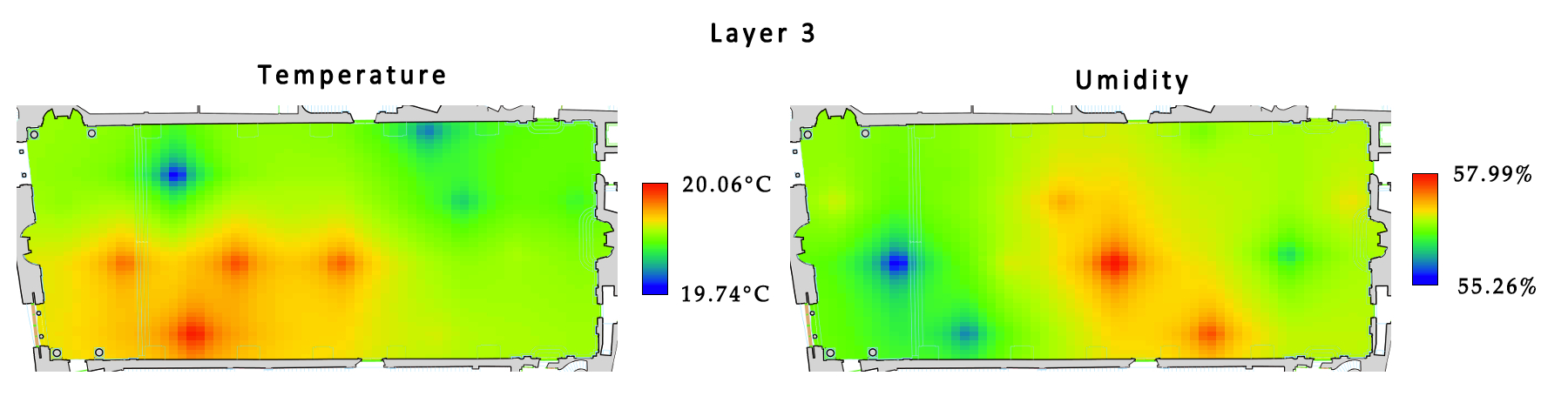
Environmental Monitoring in museums gets more complicated than usual as one can't usually install cables, attach devices, have the access to power-lineIn this context, Wireless Sensor Network is a suitable technology for non-invasive sensing of environmental conditions in proximity of artworks as frescoes, statues, paintings, etc
The installed sensors are at different heights (layers) to detect air flows and vertical profile changes. Here is an example of color map of one layer in terms of temperature and humidity
Through the analysis of environmental measurements
Scalable Methodology based on existing sensing infrastructure
This occupancy estimation methodology, designed by ELEDIA Research Center, relies on the analysis of environmental conditions. It is considered opportunistic because the system exploits common parameters, such as temperature and humidity which are not monitored neither installed for this specific estimation. The challenge consists in extracting the hidden occupancy-related information from the noisy, complex environmental data
Occupancy estimation has many applications in museums. Information about crowd flows and presence levels in the buildings can be exploited for security and safety services, marketing analysis, building automation and smart energy management
This methodology is based on the environmental parameters estimation. ELEDIA proved that the analysis of temperature and humidity vertical profiles allows to interfere the presence and the relative percentage of indoor occupancy
This Occupancy Estimation methodology is very scalable and exploit existing sensing infrastructure or designed for other applications. The system is implemented in terms of a processing software and that can be fed by any kind of sensing network
This occupancy estimation methodology, designed by ELEDIA Research Center, relies on the analysis of environmental conditions. It is considered opportunistic because the system exploits common parameters, such as temperature and humidity which are not monitored neither installed for this specific estimation. The challenge consists in extracting the hidden occupancy-related information from the noisy, complex environmental data
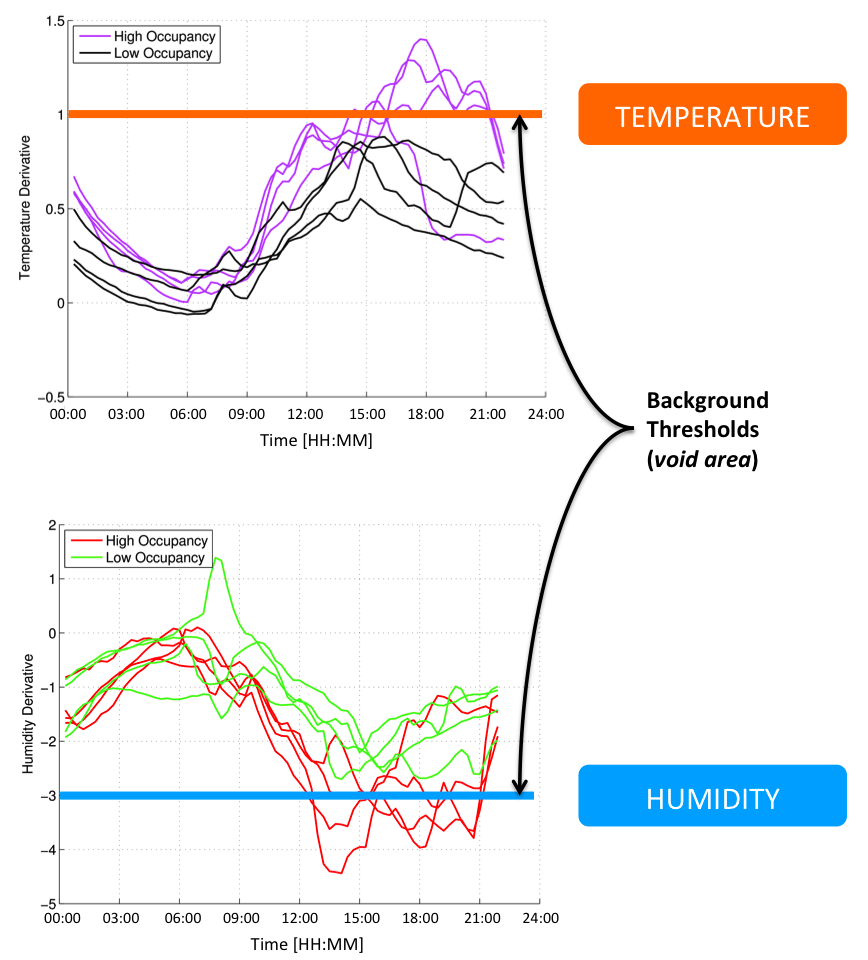
Temperature spatial derivative increases if occupancy increases
Humidity spatial derivative decreases if occupancy increases
Temperature and Humidity derivatives are flat if low occupancy
to assess the safety of artworks
Different approaches for each artworks kind
The health analysis evaluates the damage risk indicator for each kind of artworks by evaluating the measured parameters (e.g., temperature, humidity, luminosity) with respect to accordingly international guidelines (e.g., UNI 10829:1999)
It exploits machine learning for the estimation of risk index in the whole area and depending of artworks characteristics